How To Create A Two Dimensional Array In Java
An array of more than one dimension is known as a multi-dimensional array. Two of the most common examples of multi-dimensional arrays are two and three-dimensional arrays, known as 2D and 3D arrays, anything above is rare. I have never seen 4-dimensional arrays, even 3D arrays are not that common. Now the question comes when to use a multi-dimensional array? Any real-life example? Well,2D arrays are very common on platform games like Super Mario Bros to represent screen or terrain; 2D arrays can also be used to represent structures like a spreadsheet, or to draw board games like Chess, which requires an8x8 board, Checkers andTic-Tac-Toe, which requires 3 rows and 3 columns.
Another popular application of multi-dimensional arrays is in matrix manipulation. For example to represent a 3x3 matrix you need a two-dimensionalarray of 3 one-dimensional arrays each containing 3 elements.
Similarly to represent 3x2 matrices you need 2 two-dimensional arrays of a one-dimensional array of length 3. In other words, each row in a two-dimensional array is a one-dimensional array.Java truly doesn't support a multi-dimensional array but allows you to create and use an array of any number of dimensional.
A two-dimensional array is actually an array of one-dimensional array. This is unlike languages like C or FORTRAN, which allows Java arrays to have rows of varying lengths i.e. a multidimensional array can have 2 columns in one row and 3 columns in a second.
Similar to the one-dimensional array, the length of the two-dimensional array is also fixed. You can not change the length of an array, I mean, the number of rows and columns will remain fixed.
A 2x2 array can hold a total of 4 elements and they can be accessed using row and column index likea[0][0] will give you elements in the first row and first column, similarly a[1][1] will give you elements from 2nd row and 2nd column. Just like a normal array, the index starts at 0 and finishes at length -1.
Though, if you are not familiar with an essential data structure like an array and linked list, then I suggest you first go through a comprehensive fundamental course like Data Structures and Algorithms: Deep Dive Using Java on Udemy. It's a very important topic for any programmer be it a core Java developer or Java web developer and you just can not afford to ignore this.
How to Declare 2 Dimensional Array in Java? Example
If you know how to create a one-dimensional array and the fact that multi-dimensional arrays are just an array of the array in Java, then creating a 2-dimensional array is very easy. Instead of one bracket, you will use two e.g. int[][] is a two-dimensional integer array. You can define a 2D array in Java as follows :
int[][] multiples = new int[4][2]; // 2D integer array with 4 rows and 2 columns String[][] cities = new String[3][3]; // 2D String array with 3 rows and 3 columns
By the way, when you initially declare a two-dimensional array, you must remember to specify the first dimension, for example following array declaration is illegal in Java.
int[][] wrong = new int[][]; // not OK, you must specify 1st dimension int[][] right = new int[2][]; // OK
The first expression will throw the"Variable must provide either dimension expressions or an array initializer" error at compile time. On the other hand, the second dimension is optional, and even if you don't specify compiler will not complain, as shown below :
String[][] myArray = new String[5][]; // OK String[][] yourArray = new String[5][4]; // OK
This is possible because a two-dimensional array in Java is nothing but an array of a one-dimensional array, because of this, you can also create a two-dimensional array where individual one-dimensional arrays have different lengths, as seen in the following example.
class TwoDimensionalArray { public static void main(String[] args) { String[][] salutation = { { "Mr. " , "Mrs. " , "Ms. " }, { "Kumar" } }; // Mr. Kumar System.out.println(salutation[0][0] + salutation[1][0]); // Mrs. Kumar System.out.println(salutation[0][1] + salutation[1][0]); } } The output from this program is: Mr. Kumar Mrs. Kumar
In this example, you can see that salutation is a 2D array but its first row has 3 elements while the second row has just one element.
You can access elements of a two-dimensional array either by using both indexes or just one index. For examplesalutation[ 0 ][ 1 ] represents a Single String in Java, whilesalutation[ 0 ] represents a one-dimensional array ( a single row in the 2-dimensional array). You can further seeAlgorithms and Data Structures - Part 1 and 2 courses on Pluralsight to learn more about it.
How to Initialize Two Dimensional Array in Java? Example
So far we have just declared and created the array, we haven't initialized them. This means all elements of the array have their default values e.g. zero for an array of integral values likebyte, short, char,and int,0.0 for floating-point arrays like float and double, false for boolean arrays, and null for an array of reference type like String array elements.
You can verify this by accessing the first element of a two-dimensional array as multiples[0][0], which will print zero, as shown below:
boolean[][] booleans = new boolean[2][2]; System.out.println( "booleans[0][0] : " + booleans[0][0]); byte[][] bytes = new byte[2][2]; System.out.println( "bytes[0][0] : " + bytes[0][0]); char[][] chars = new char[1][1]; System.out.println( "chars[0][0] : " + (int)chars[0][0]); short[][] shorts = new short[2][2]; System.out.println( "short[0][0] : " + shorts[0][0]); int[][] ints = new int[3][2]; System.out.println( "ints[0][0] : " + ints[0][0]); long[][] longs = new long[2][2]; System.out.println( "longs[0][0] : " + longs[0][0]); float[][] floats = new float[1][2]; System.out.println( "floats[0][0] : " + floats[0][0]); double[][] doubles = new double[2][2]; System.out.println( "doubles[0][0] : " + doubles[0][0]); Object[][] objects = new Object[2][2]; System.out.println( "objects[0][0] : " + objects[0][0]); Output booleans[0][0] : false bytes[0][0] : 0 chars[0][0] : 0 short[0][0] : 0 ints[0][0] : 0 longs[0][0] : 0 floats[0][0] : 0.0 doubles[0][0] : 0.0 objects[0][0] : null
You can see the default values of different types of primitive arrays here. Character array is a bit tricky because if you print 0 as a character it will print a null character and that's why I have used its integer value by casting to int.
Now there are two ways to initialize a two-dimensional array in Java, either by using an array literal at the time of creation or by using nested for loop and going through each element.
In the next example, we will learn how to loop through a two-dimensional array, initialize each element and how to print a two-dimensional array in Java:
// initializing two dimensional array as literal String[][] names = { { "Sam" , "Smith" }, { "Robert" , "Delgro" }, { "James" , "Gosling" }, }; // how to initialize two dimensional array in Java // using for loop int[][] board = new int[3][3]; for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) { board[i][j] = i + j; } }
In the first example, we have created and initialized a String array using an array literal, while in the second example we have created a two-dimensional array board, and later initialized it by looping through the array. You can further seeObject-Oriented Java Programming: Data Structures and Beyond Specialization on Coursera to learn more about how to use an array and other data structures in real-world projects.
How to Loop and Print 2D array in Java? Example
If you want to access each element of a two-dimensional array, then you need to iterate through the two-dimensional array using two for loops. Why? because you need two indexes to access an individual element from the 2D array. You can either use advanced for each loop or classic for loop with a counter.
The second one is more powerful as it provides an explicit counter which can be used as indexes. To print the contents of a two-dimensional array, you can either use this method or can use Arrays.deepToString() method, which will return a String version of all elements of a 2D array, as shown in the following example.
import java.util.Arrays; /** * Java Program to initialize and print two dimensional array in Java. * * @author WINDOWS 8 * */ class Basics { public static void main(String args[]) { // initializing two dimensional array as literal String[][] names = { { "John" , "Smith" }, { "Javin" , "Paul" }, { "James" , "Gosling" }, }; // how to initialize two dimensional array in Java // using for loop int[][] board = new int[3][3]; for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) { board[i][j] = i + j; } } // now let's print a two dimensional array in Java for (int[] a : board) { for (int i : a) { System .out.print(i + " \t " ); } System .out.println( " \n " ); } // printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method System .out.println( "another way to print 2D arrays" ); System .out.println(Arrays .deepToString(board)); } } Output : 0 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 another way to print 2D arrays [[0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4]]
This was an important trick to learn while working with Array in Java. If you want to learn more such tricks, you can also join the Data Structures and Algorithms Specialization on Coursera. It's a free course to audit but you need need to pay if you need certification. This course will teach you algorithms through programming and help you to advance your software engineering or data science career
Important Points about Multi-dimensional Array in Java
1) Java doesn't support a multi-dimensional array in the true sense. In a true two-dimensional array, all the elements of the array occupy a contiguous block of memory, but that's not true in Java. Instead, a multi-dimensional array is an array of array.
For example, a two-dimensional array in Java is simply an array of a one-dimensional array, I meanString[][] is an array of String[] or "array of array of strings".
This diagram shows how exactly two-dimensional arrays are stored in Java :
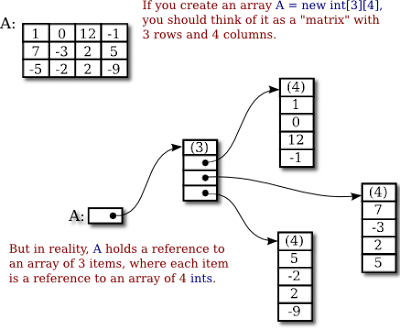
2) Because of the above reason, the second dimension in an array is optional in Java. You can create a two-dimensional array without specifying both dimensions likeint[4][] is a valid array declaration. It also allows you to create a multi-dimensional array whose rows can vary in length, as we have seen in our second example.
3) While creating two dimensional or three-dimensional array in Java, the first dimension is a must, without that compile will throw an error e.g. int[][3] is Not Ok but int[3][] is Ok.
4) A two-dimensional array is a very useful data structure in game programming. You can use it on tile-based games like Super Mario Bros to draw terrain, background, and other objects, on games like Tetris to represent the playing areas.
A 2D array is also very useful in matrix manipulation. You can use a 2D array to represent any matrix and perform addition, multiplication, and other operations. A 2D array can also be used to represent any object in plain using X and Y coordinates.
Similarly, 3D arrays can be used to represent things in three-dimensional space using X, Y, and Z coordinates. Some of the popular examples of two-dimensional arrays are chess board, checkers board, and other board games which have slots. You can view the chessboard as an array of 8 rows and 8 columns.

5) There are multiple ways to define and initialize a multidimensional array in Java, you can either initialize them using in the line of declaration or sometime later using a nested for loop. You will need as many for a loop as many dimensions of the array you have. For example to explicitly initialize a three-dimensional array you will need three nested for loops. On the other hand, to initialize a 2D array, you just need two nested loops.
6) In a two dimensional array likeint [][] numbers = new int [ 3 ][ 2 ], there are three rows and two columns. You can also visualize it like a 3 integer arrays of length 2. You can find the number of rows using numbers.length and number of columns using numbers[0].length expression, as shown in the below example. This is also very useful while iterating over a two-dimensional array in Java.
int[][] primes = new int[3][2]; int rows = primes.length; // 3 int cols = primes[0].length; // 2 System.out.printf( "int[3][2] has %s rows and %d columns %n " , rows, cols); Output : int[3][2] has 3 rows and 2 columns
That's all about multi-dimensional array in Java. It is one of the useful data structures, especially to represent two-dimensional things like a matrix. It is also very useful to build tile-based games. By the way, It's worth remembering that Java doesn't support true multi-dimensional arrays, instead, they are represented as "array of array".
Do you want to learn more about the array data structure? The most important Data structure for a programmer - If Yes, here are a couple of more articles which you can explore to learn about Array better:
- 20+ String Coding Problems from Interviews (questions)
- How to create an array from ArrayList of String in Java (tutorial)
- 100+ Data Structure Problems from Interviews (questions)
- Top 30 Array-based Coding Problems from Interviews (questions)
- How to remove duplicates from an unsorted array in Java? (solution)
- 10 Data Structure Courses to Crack Programming Interviews (courses)
- How to find all pairs whose sum is equal to a given number in an array? (solution)
- How to reverse an array in place in Java? (solution)
- 10 Algorithms Books Every Programmer Should Read (books)
- 10 Free Data Structure and Algorithm Courses for Beginners (courses)
- Top 20 Searching and Sorting Interview Questions (questions)
- How to make a binary search tree in Java? (solution)
- 10 (Free) Online Courses to Learn Data Structure and Algorithms in Java (courses)
- 50+ Data Structure and Algorithms Interview Questions (questions)
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this two-dimensional array tutorial then please share it with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions or feedback then please drop a note.
P. S. - If you are looking to learn Data Structure and Algorithms from scratch or want to fill gaps in your understanding and looking for some free courses, then you can check out this list of Free Algorithms Courses from Udemy and Coursera to start with.
How To Create A Two Dimensional Array In Java
Source: https://www.java67.com/2014/10/how-to-create-and-initialize-two-dimensional-array-java-example.html
Posted by: boothereastill.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create A Two Dimensional Array In Java"
Post a Comment